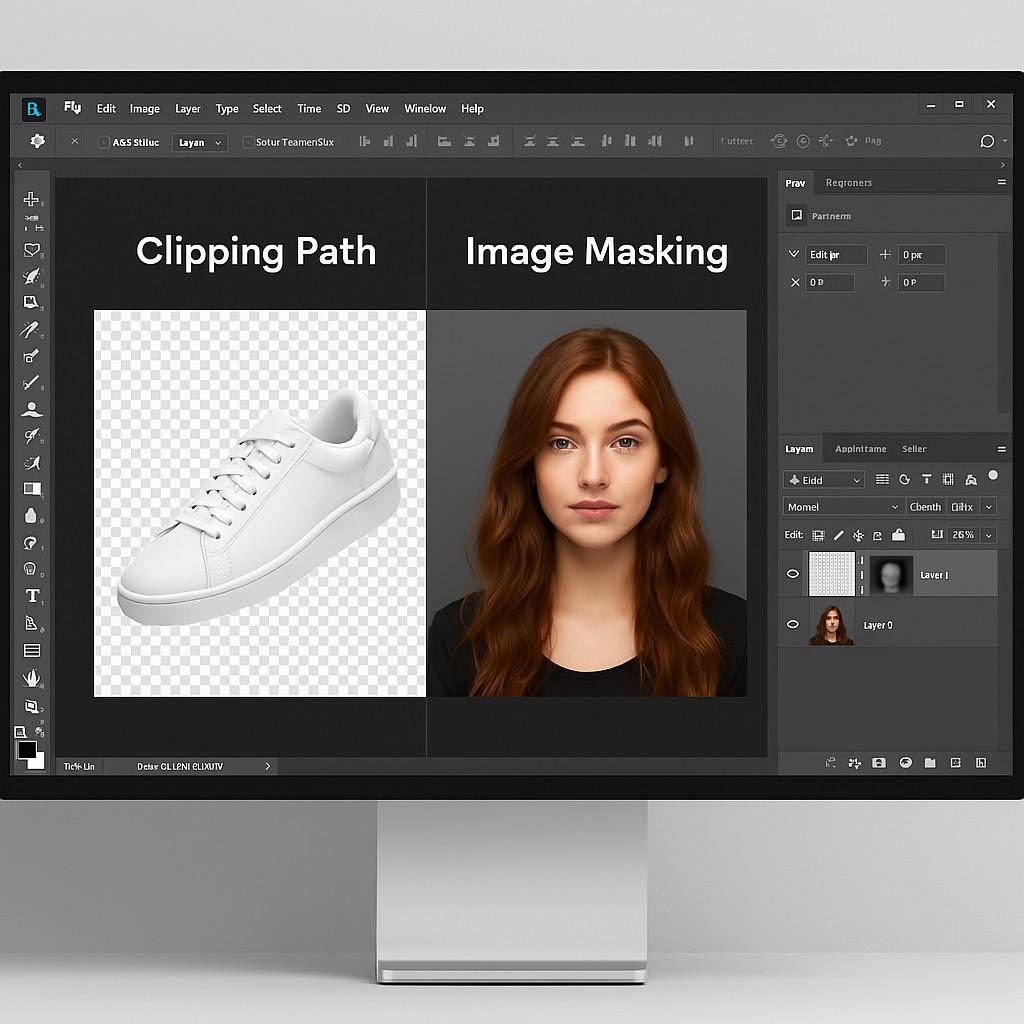
Clipping Path vs. Image Masking: Which One Do You Need?
Do you know the difference between clipping path vs. image masking? It is essential for producing clean, professional visuals. Both techniques are used to isolate subjects from their backgrounds, but they work in different ways and serve different purposes. A clipping path uses a vector outline for sharp-edged objects, while image masking handles fine details like hair or transparent areas.
These methods are especially important in industries such as e-commerce, advertising, and publishing, where high-quality product photos and visual content are crucial. Choosing the right approach helps ensure accuracy, consistency, and a polished final image.
Clipping Path vs. Image Masking: Which One Do You Need?
When editing product images or preparing visual content, choosing between clipping path vs. image masking is a key decision. Both techniques are used to remove backgrounds or isolate subjects, but they differ in approach and application. Knowing when to use each method is important for achieving clean, professional results in industries like e-commerce, fashion, and advertising.
Clipping path works best for sharp-edged objects and precise cutouts, while image masking is ideal for complex edges like hair, fur, or semi-transparent materials. Understanding the tools, methods, and limitations of each helps editors maintain image quality and consistency.
What Is a Clipping Path?

A clipping path is a manually drawn vector outline used to separate an object from its background. It is created using the Pen Tool in image editing software like Adobe Photoshop. This technique keeps the area inside the path visible and removes everything outside.
Best used for:
- Products with hard, defined edges (e.g., electronics, furniture)
- Simple to moderately complex shapes
- High-precision cutouts for catalogs or web listings
Clipping path is widely used in commercial product photography, especially where clean lines and accurate edges are essential.
Common Clipping Path Techniques

- Basic Pathing: For simple geometric objects
- Compound Paths: For items with holes or multiple cutouts
- Multi-Path Editing: Allows color correction or adjustment of specific image sections
These techniques give editors control over shape, edge quality, and layering for complex visual needs.
What Is Image Masking?

Image masking is a technique that hides or reveals parts of an image using pixel-level control. It’s often used when the subject has fine details that are difficult to isolate with a clipping path, such as soft edges, transparency, or overlapping textures.
Best used for:
- Hair, fur, feathers, or fabric
- Transparent or semi-transparent objects (e.g., glass, smoke)
- Soft-edged selections that require smooth blending
Masking allows greater flexibility and accuracy when working with detailed or partially transparent subjects.
Types of Image Masking Techniques
- Layer Masking: Non-destructive editing that hides or reveals parts of an image
- Alpha Channel Masking: For objects with transparency or fine edges
- Refine Edge/Select and Mask: Advanced tools to improve selection smoothness and edge detail
These methods are essential in high-end image retouching, especially for fashion, beauty, and advertising work.
Key Differences Between Clipping Path and Image Masking

Knowing the distinctions between these two techniques helps ensure the right method is used for the right type of image:
| Feature | Clipping Path | Image Masking |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Vector path using the Pen Tool | Pixel-based selection and masking |
| Best For | Sharp-edged, solid objects | Soft, transparent, or complex edges |
| Output Precision | High accuracy for clean shapes | Smooth transitions and fine details |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, but very precise | More adaptable for blending and effects |
| Common Uses | E-commerce, product photos | Fashion, hair, glass, and creative edits |
When to Use Each Method
Use a clipping path when the object has smooth, defined edges and no transparency. Use image masking when working with soft edges or partially transparent objects. In many cases, both methods may be combined for best results, clipping path for the main outline and masking for detailed or soft sections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) On Clipping Path vs. Image Masking
1. What is the main difference between clipping path and image masking?
✅ Clipping path uses vector outlines for sharp-edged objects.
✅ Image masking handles soft edges like hair or transparent materials.
❌ Clipping path isn’t ideal for complex edges.
❌ Image masking isn’t suitable for simple, hard-edged products.
2. When should I use a clipping path?
✅ Use for products with clean, sharp edges like electronics, shoes, and furniture.
✅ Ideal for e-commerce product listings and print catalogs.
❌ Not recommended for hair, fur, or transparent items.
3. When is image masking better than a clipping path?
✅ Best for images with soft edges—hair, feathers, fur, fabric, or smoke.
✅ Suitable for transparent or semi-transparent products like glass or water.
❌ Not necessary for solid, well-defined objects.
4. Can I use both clipping path and image masking together?
✅ Yes! Many professional editors combine both methods for the best results.
✅ Clipping path for clean outlines and image masking for complex edges.
✅ This approach improves precision and flexibility in photo editing.
5. Which industries use clipping paths and image masking the most?
✅ Clipping path: E-commerce, fashion product photography, and advertising.
✅ Image masking: Beauty, fashion, creative ads, and transparent product showcases.
✅ Both are essential in professional photo retouching services.
6. Does image masking affect image quality?
✅ No, when done properly, image masking maintains high quality and natural looks.
❌ Poor masking can cause blurring or unwanted edges—professional skills are key.
Conclusion
Both clipping path and image masking are essential tools in professional image editing, each suited to different types of visual content. Clipping path offers precise cutouts for objects with clear, defined edges, while image masking handles complex edges, soft transitions, and transparency with greater flexibility.
Understanding the comparison of clipping path vs. image masking: which one do you need? helps professionals choose the most appropriate technique based on the subject and intended use. In industries like e-commerce, fashion, and graphic design, selecting the right method supports consistent, high-quality visual output across various platforms.
Suggested Reads
✅ How to Improve Product Photos with Clipping Path Services
Explore effective ways to elevate your product images using professional clipping path techniques.
✅ Clipping Path vs Image Masking: When to Use Which?
Go deeper into decision-making with extra examples of when each method shines.