Clipping Path vs. Image Masking: When to Use Which?
Clipping Path and Image Masking are both essential techniques in image editing, each serving distinct purposes based on the complexity and nature of the subject. Here’s a detailed comparison to help you determine when to use each:
Clipping Path
Definition: A vector-based method that involves drawing a closed path around an object to isolate it from the background.
Best For: Objects with sharp, well-defined edges such as products, logos, and geometric shapes.
Tools Used: Pen Tool in Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator
Advantages:
· Provides precise and clean edges.
· Ideal for bulk editing, especially in e-commerce.
· Scalable without loss of quality, suitable for print and digital media.
Disadvantages:
· Not suitable for complex or soft-edged objects like hair or fur.
· Once applied, edits are permanent unless the path is saved for future adjustments.
When to Use:
· Removing backgrounds from product photos, logos, or illustrations.
· Creating assets for catalogs, advertisements, or websites.

Image Masking
Definition: A pixel-based technique that hides or reveals parts of an image using masks, allowing for soft transitions and intricate details.
Best For: Subjects with fine details and soft edges, such as hair, fur, smoke, or semi-transparent objects.
Tools Used: Layer Masks, Brush Tool, Channels in Adobe Photoshop.
Advantages:
- Retains fine details and soft edges.
- Non-destructive editing, preserving the original image data.
- Allows for continuous adjustments and refinements.
Disadvantages:
- More complex and time-consuming.
- Requires a higher level of skill and understanding of masking techniques.
When to Use:
- Editing portraits, fashion photography, or images with intricate details.
- Handling semi-transparent objects like glass, veils, or smoke.
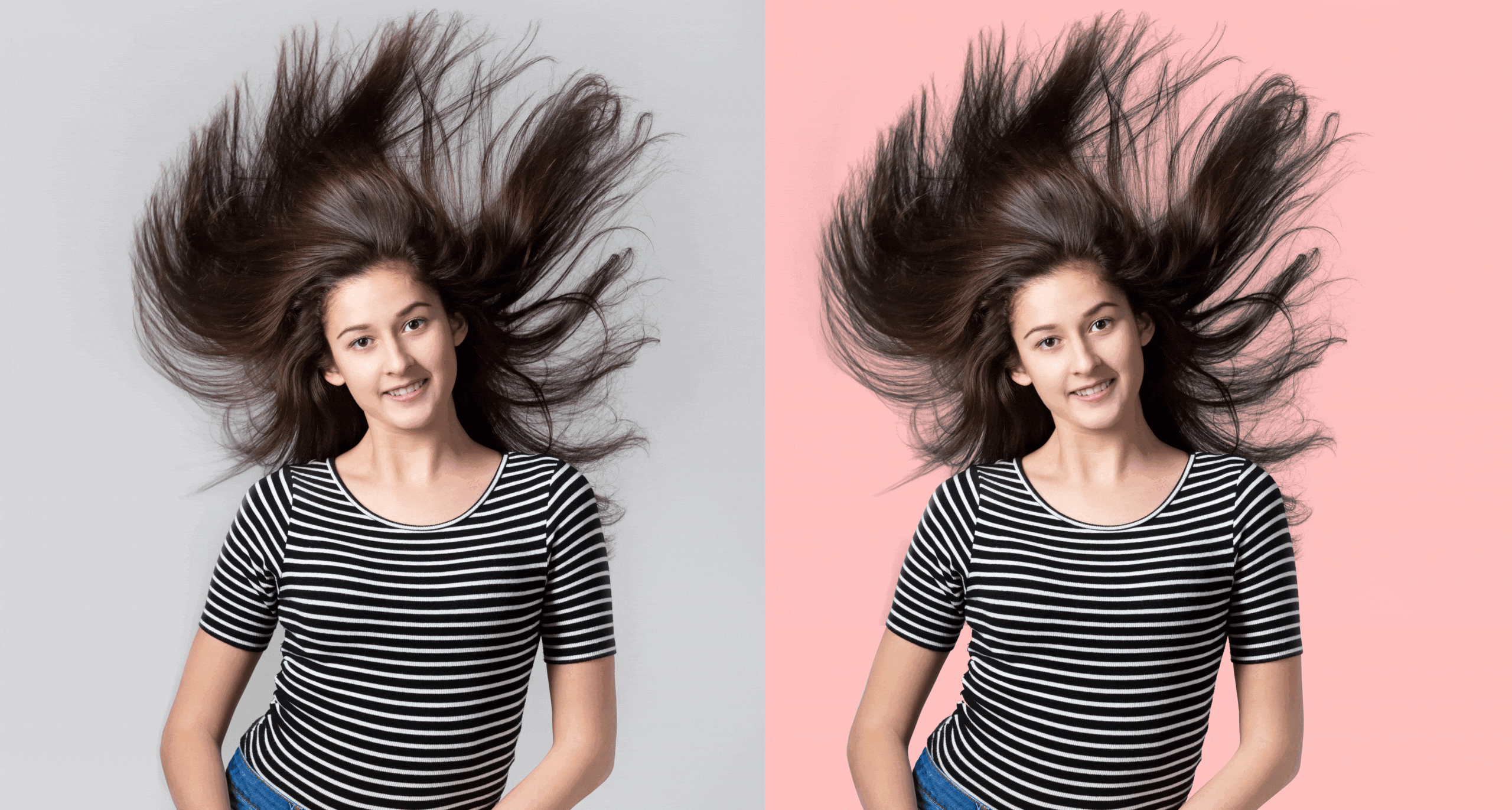
Comparison Table
| Feature | Clipping Path | Image Masking |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Vector-based | Pixel-based |
| Best For | Hard-edged objects | Soft-edged or detailed subjects |
| Tools Used | Pen Tool | Layer Masks, Brush Tool, Channels |
| Edge Handling | Precise, clean edges | Soft, blended edges |
| Transparency | Limited | Handles semi-transparency well |
| Editing Flexibility | Less flexible post-application | Highly flexible and non-destructive |
| Common Use Cases | Product photos, logos, and illustrations | Portraits, fashion, and transparent objects |
FAQs: Clipping Path vs. Image Masking
1. What is the difference between clipping path and image masking?
A clipping path uses Photoshop’s Pen Tool to create a precise outline around objects with hard edges (e.g., jewelry, electronics) for background removal. Image masking employs layer masks or alpha channels to isolate complex objects with soft edges, like hair or fur, ensuring detailed cutouts.
2. When should I use clipping path vs. image masking?
Use clipping path for products with clean, defined edges (e.g., watches, bottles) for sharp, quick cutouts. Opt for image masking when editing complex subjects like apparel, hair, or fur to preserve intricate details. Clipping paths suit simple e-commerce products, while masking excels for detailed images.
3. Can I use clipping path for complex objects like hair?
Clipping paths are not ideal for complex objects like hair or fur due to their intricate edges. Image masking, particularly alpha channel masking, is better for detailed cutouts, ensuring natural-looking results for e-commerce product photos with soft or fuzzy edges.
4. Is AI background removal better than clipping path or image masking?
AI background removal is faster and cost-effective for simple images but may lack precision for complex subjects like hair or transparent objects. Manual clipping paths and image masking offer superior control and quality for professional e-commerce product photography.
5. How much does clipping path or image masking cost for e-commerce?
Clipping path services typically cost $0.25–$1 per image for simple objects, while image masking for complex subjects like hair ranges from $1–$5 per image. DIY editing in Photoshop is free but time-intensive, making professional services ideal for bulk editing.
6. What tools are best for clipping path and image masking?
Adobe Photoshop is the go-to tool, using the Pen Tool for clipping paths and Layer Masks or Alpha Channels for image masking. Free alternatives like GIMP can work but offer less precision, making Photoshop the industry standard for e-commerce photo editing.
7. Can clipping path or image masking be used for Amazon product photos?
Yes, clipping paths are perfect for creating clean, white-background images required by Amazon. Image masking is ideal for apparel or products with complex edges, ensuring professional-quality cutouts that meet Amazon’s strict image guidelines.
8. How long does it take to edit a product photo with clipping path or masking?
Clipping path editing takes 5–15 minutes per image for simple objects, while image masking for complex subjects like hair can take 20–60 minutes. Professional services, like those from Pixc, offer turnarounds in as little as 6 hours for bulk orders.
9. Why outsource clipping path or image masking for product photography?
Outsourcing saves time, ensures consistent high-quality results, and is cost-effective for e-commerce businesses. Professional services deliver precise cutouts optimized for platforms like Amazon, Shopify, or Etsy, allowing you to focus on growing your business.
Conclusion
Use Clipping Path : When dealing with objects that have clear, defined edges and require precise background removal, such as product photography or logos.
Use Image Masking : When working with subjects that have intricate details or soft edges, like hair, fur, or semi-transparent materials, to ensure high-quality and realistic results.
In some cases, combining both techniques—using a clipping path for the main object and masking for detailed areas—can yield the best results.
If you need assistance with specific image editing tasks or further guidance on choosing the appropriate technique, feel free to ask!
Suggested Reads
✅ Clipping Path vs. Image Masking: Which One Do You Need?
Confused about clipping path or masking? Discover the right photo editing method for your product images.
✅ Background Removal vs Clipping Path: What’s the Difference?
Learn the key differences between background removal and clipping path to choose the perfect solution for flawless photos.
✅ How to Improve Product Photos with Clipping Path Services
Boost your product images with expert clipping path techniques. Find out how professionals enhance photo appeal instantly.
✅ Benefits of Using a Professional Clipping Path Service
Explore the top benefits of hiring professional clipping path services for clean, polished, and market-ready product photos.
✅ Clipping Path Service for E-commerce
Running an online store? Discover why clipping path services are essential for high-converting e-commerce product images.
✅ Clipping Path Service Provider
Looking for the best clipping path expert? Here’s how to choose a reliable clipping path service provider for your business.
✅ The Best Clipping Path Service
See what makes a clipping path service the best! Discover features and tips to get the most out of your photo edits.



